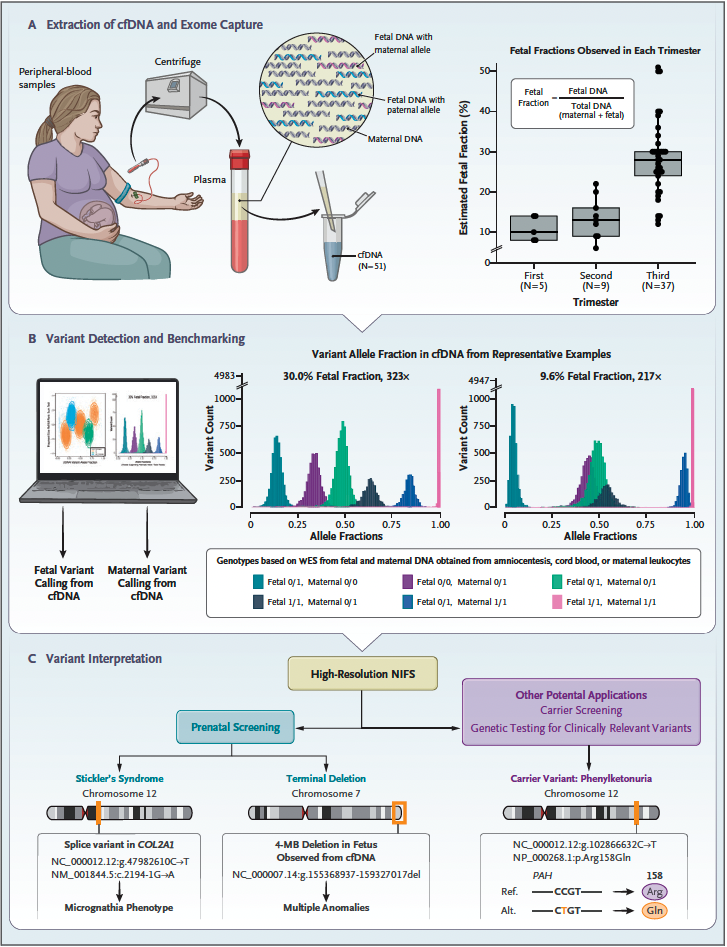
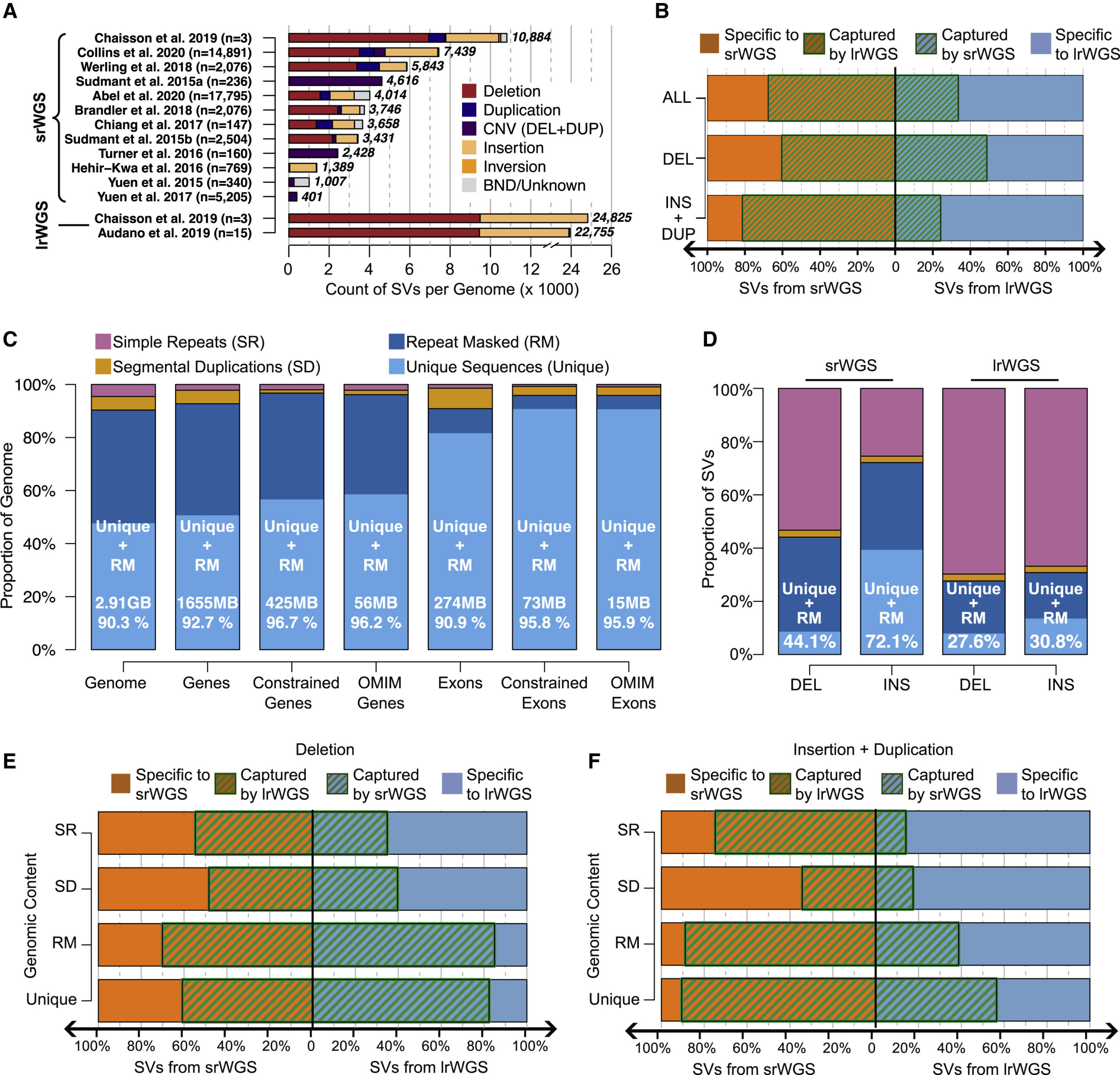
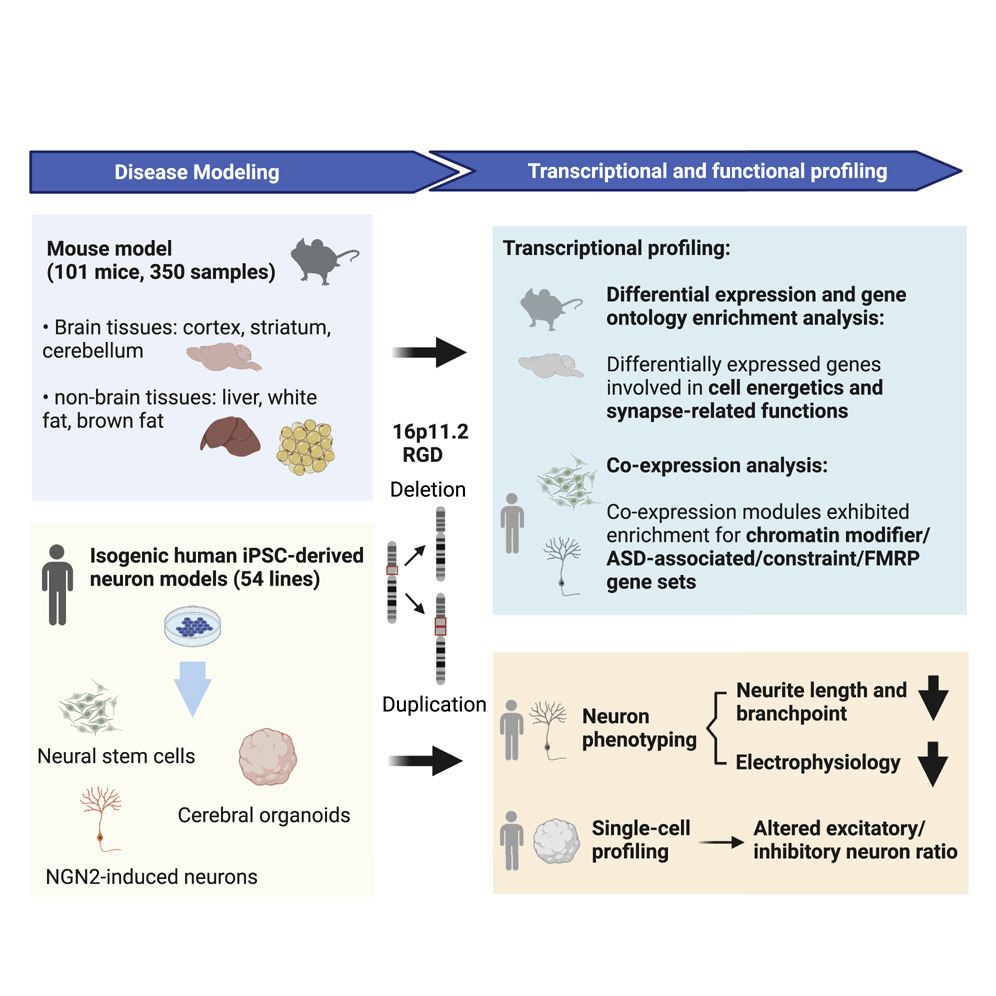
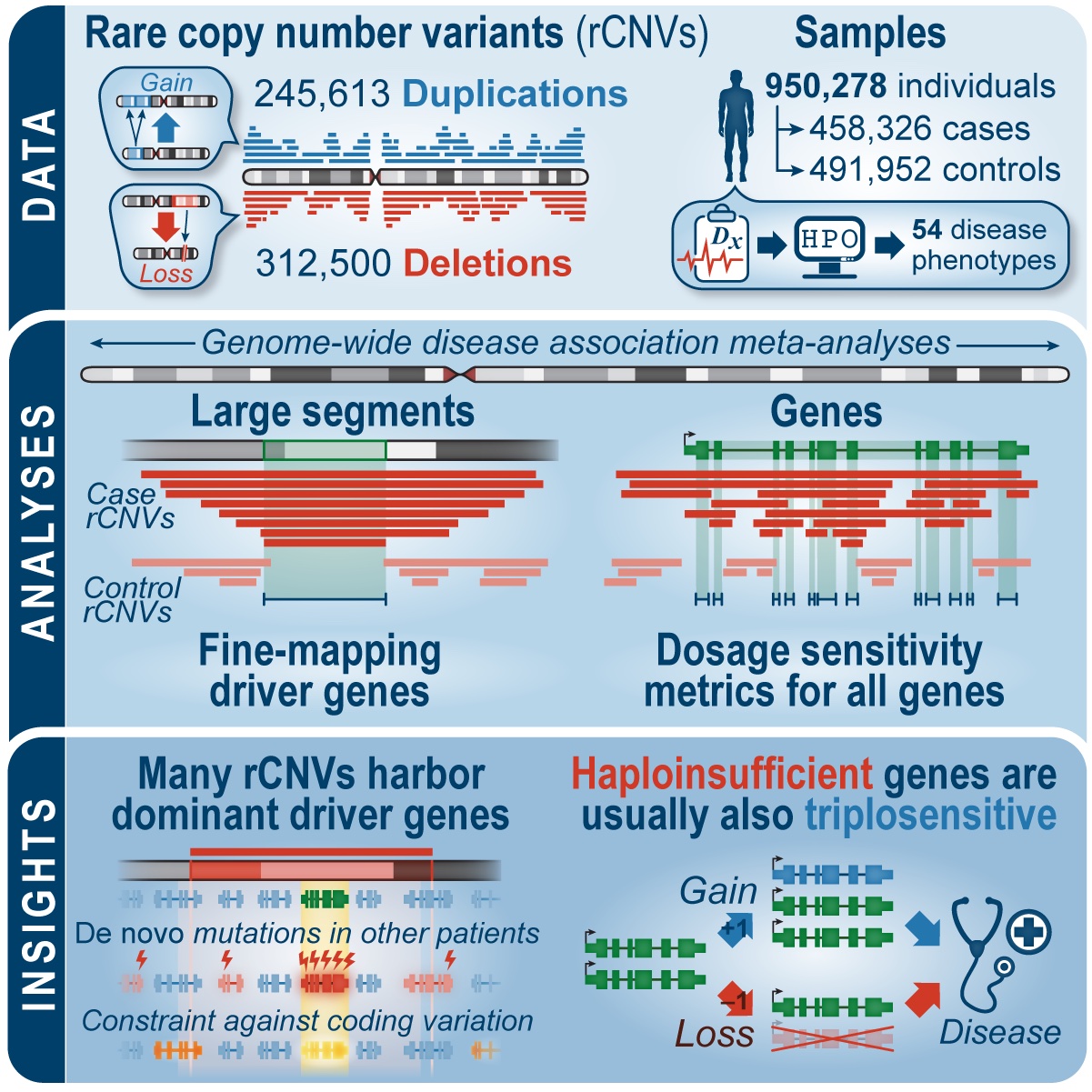
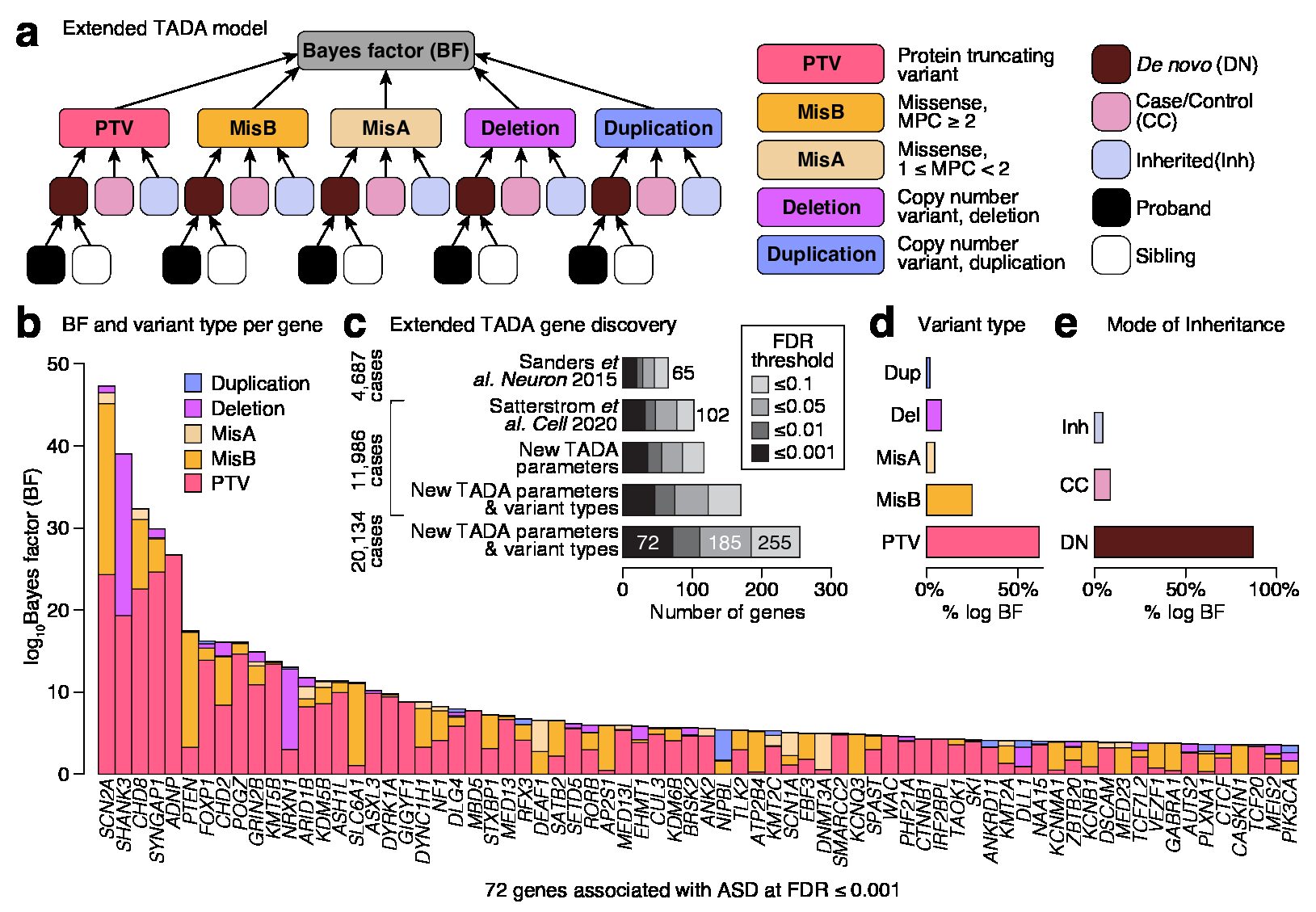
Enhancing the possibilities of prenatal genetic testing through non-invasive fetal sequencing (NIFS)
The current standard of care for fetal genetic testing requires an invasive medical procedure such as amniocentesis to survey individual DNA changes in the fetal genome. Here, the Talkowski laboratory has developed a new technology that enables pregnant persons to screen the protein-coding sequence of all genes in the fetal genome from a simple blood [...]